Nurul Nasuha Husain, Ezatul Ezleen Kamarulzaman, and Habibah A. Wahab
Background
Obesity is defined as body mass index (BMI) exceeding 30, whereas overweight is referred to a BMI value between 25 and 29.9. Epidemiology studies stated that increasing degrees of overweight and obesity is a crucial prognostic of decreased longevity. Obesity is a multifactorial and heterogeneous syndrome affected from environmental factors and genetic susceptibility (1). The environmental factors are mainly due to daily diet. Fat-rich diet will cause excess triacylglycerol in the body (2).
Obesity is associated to several diseases such as gallbladder disease, endocrine and metabolic disturbances, cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes mellitus, hypertension pulmonary disease, gout osteoarthritis and also psychological problems (3). There are few strategies of treating obesity such as medication, behavioral and dietary modification, exercise and gastric bypass surgery in utmost cases. Despite all the efforts and remedies provided by diet industry, they failed to give long-term effect of weight loss for obese or overweight people. Individuals who are changing their diet to lose weight were estimated to return to their original weight within 2 to 5 years (4).
Generally there are five strategies to control and overcome obesity.. First strategy is inhibition of pancreatic lipase. Digested dietary triacylglycerol are hydrolyzed to fatty acid and monoacylglycerol and absorbed by small intestine. Excess triacylglycerol in the body will accumulate in the adipose tissue causing obesity. Thus inhibition of lipase restrained the dietary fat from being hydrolysed and absorbed into the intestine. The second strategy involves the suppression of food intake to regulate body weight, which related to hormonal and neurological system. The third strategy is stimulation of energy expenditure is to modulate energy expenditure and body weight by increasing energy expenditure via physical activity, obligatory energy expenditure or by adaptive thermogenesis. Fourth strategy is adipocyte proliferation and differentiation, which is important in maintaining energy balance and lipid homeostasis. Lastly, the regulation of lipid metabolism by prompting triglyceride hydrolysis is to decrease fat store in the body (5).
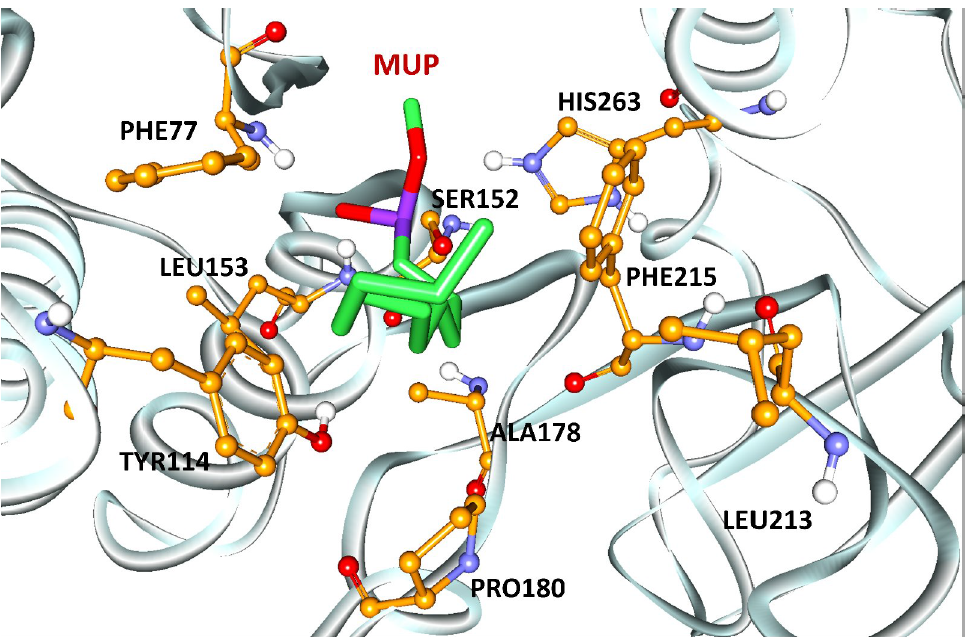
Figure 1. Bound inhibitor, methoxyundecylphosphinic acid (MUP) in active site, surrounded by essential key amino acids for inhibition of pancreatic lipase (7).
There are many authorized drugs for treatment of obesity available in the market. However, some drugs for obesity treatment may have serious health problem. Orlistat, or also known as Xenical, act by blocking the digestion of dietary fat can give side effects to consumer, such as diarrhea, gas, stomach pain and rare cases of severe liver injury. Lorcaserin, sold as Belviq is an appetite suppressant drug. Lorcaserin have reported to have side effects such as constipation, dry mouth, cough, tiredness, nausea dizziness and headaches. Phentermine-topiramate is also an appetite suppressant drug. The side effects of this drug are constipation, dry mouth, insomnia, dizziness, taste alterations and tingling of hands and feet (6).
Methods
In this study, in-silico screening has been chosen to study inhibition of pancreatic lipase, an enzyme responsible for hydrolysis of dietary fat. Pancreatic lipase structure, 1LPB, was retrieved from Protein Data Bank along with methoxyundecylphosphinic acid (MUP) as inhibitor. For validation, control docking was performed between covalently bonded inhibitor, MUP and pancreatic lipase. The root-mean square deviation (RMSD) of control docking is 1.37 with free energy of binding of -2.55kcal/mol. The searching of potential compounds for anti-obesity was carried out by screening Malaysian native plant database, NADI (www.nadi-discovery.com), via molecular docking of those plants’ chemical substances against pancreatic lipase. From docking analysis, inophyllum E from the bark of Calophyllum inophyllum, commonly known as laurelwood is predicted to have highest inhibitory activity based on the free energy of binding, -12.85 kcal/mol. Other plants that have bioactive compounds, potentially to be an inhibitor for pancreatic lipase are Costus speciosus (leaves), Artocarpus champeden (bark), Aglaia lawii (bark), Oryza sativa, Lansium domesticum (bark) and Dysoxylum hainanense (bark) with free energy of binding -12.79, -12.55, -12.20, -12.18, -12.15 and -12.09 kcal/mol, respectively. This energy was contributed by molecular interactions between the NADI’s compounds with essential amino acid residues for activity of the lipase such as Gly76, Phe77, Ile78, Asp79, Arg111, Tyr114, His151, Ser152, Ala178, Pro180, Phe215, Arg256 and His263.
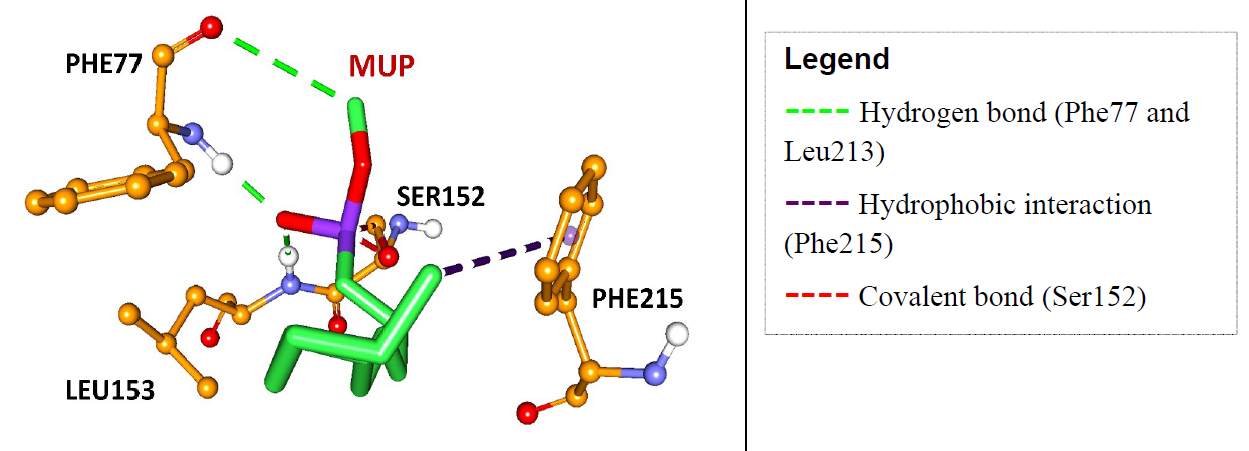
Figure 2. Interaction between MUP and amino acids.
In-silico experiment was carried out using Autodock Tools version 1.5.6 and Autodock 4.2. Visualization and analysis of interaction between chemical compounds and pancreatic lipase was done using Discovery Studio 4.0 Visualizer.
Conclusion
Molecular docking gives an understanding of an insight molecular mechanism of bioactive compounds in Malaysia plants as pancreatic lipase inhibitors. These bioactive compounds can be further tested as potential inhibitors and treatment for obesity. Five compounds from different plants will be further tested for in-vitro study. The compounds are inophyllum E from the bark of Calophyllum inophyllum, β-sitosterol glucoside from leaves of Costus speciosus, artonin B from bark of Artocarpus champeden, poriferasterol from bark of Aglaia lawii, 7-oxostigmasterol from Oryza sativa, 8,14-Secogammacera-7,14(27)-diene-3,21-dione-8,14-secogammacera-7,14diene5 3,21-dione(isomer 2) from bark of Lansium domesticum and 24,25-Epoxy-3-beta,23-dihydroxy- 7-tirucallene from bark of Dysoxylum hainanense.



Add new comment